Load Balancing
Load balancing is the process of distributing workloads evenly across multiple servers, resources, or applications to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The goal of load balancing is to distribute the workload in such a way that no single server becomes overwhelmed.
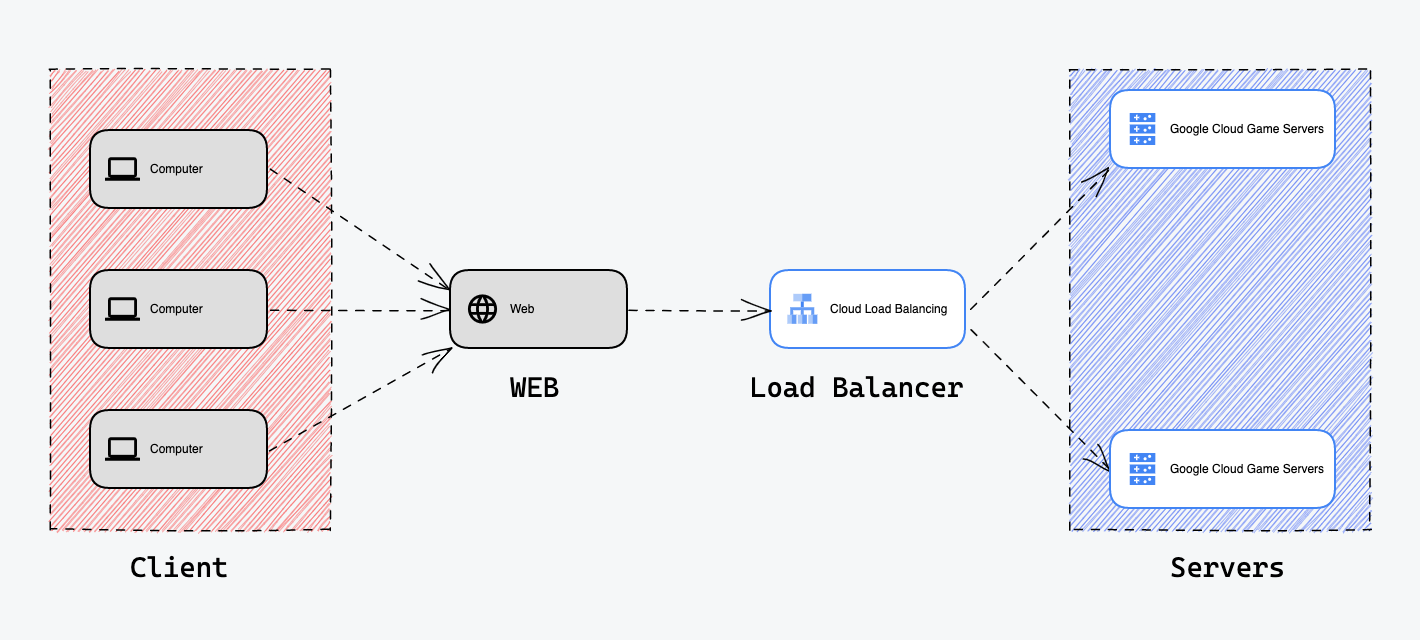
Real-World Analogy:
A real-world analogy for load balancers is a traffic cop directing vehicles at a busy intersection. The traffic cop's job is to ensure that the flow of traffic is evenly distributed among the different roads, preventing any one road from becoming overwhelmed and causing a traffic jam. Similarly, a load balancer's job is to distribute incoming requests among multiple servers, preventing any one server from becoming overwhelmed and causing a system failure.
Like a traffic cop, the load balancer is constantly monitoring the traffic (or incoming requests) and making decisions on where to route the traffic based on certain rules and algorithms. The traffic cop and the load balancer both play a vital role in ensuring that the flow of traffic/requests is managed efficiently and effectively.
Load Balancing Algorithms
There are several commonly used algorithms in load balancing, here are a few examples:
- Round Robin: One of the most basic and widely used algorithms, it distributes incoming requests to a group of servers by taking turns in a cyclical order.
- Random: This algorithm routes incoming requests to a random server
- Least Connections: This algorithm routes incoming requests to the server with the least number of active connections.
- Least Response Time: This algorithm routes incoming requests to the server with the least response time, measured by a health check.
- Weighted Round Robin: This algorithm is similar to Round Robin but gives more weightage to some servers over others.
- IP Hash: This algorithm routes incoming requests to a specific server based on a hash of the client's IP address.
Pros and Cons:
Pros of Load Balancing:
| Pros | Description |
|---|---|
| Improve performance | By distributing incoming traffic among multiple servers, load balancing can help to prevent any one server from becoming overwhelmed and improve overall system performance. |
| Increase availability | By providing redundancy and failover capabilities, load balancing can help to increase the availability of the system and ensure that it remains up and running even in the event of a server failure. |
| Scalability | Load balancing enables the system to handle an increasing number of requests without becoming overwhelmed, making it easier to scale the system as needed. |
| Flexibility | Load balancing can be done at different layers of the OSI model, and there are various algorithms and types of load balancing to choose from, making it a flexible solution that can be adapted to the specific requirements of the system. |
Cons of Load Balancing:
| Cons | Description |
|---|---|
| Complexity | Load balancing can be a complex process, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise to set up and maintain. |
| Extra hardware or software costs | Depending on the type of load balancing used, additional hardware or software may be required, which can add extra costs to the system. |
| Single point of failure | If the load balancer itself fails, the entire system can become unavailable. It's important to have a backup load balancer to minimize this risk |
| Additional Latency | Load balancers can introduce additional latency due to the time it takes to evaluate the requests and route them to the appropriate server. |
It's important to note that load balancing can be a complex process and it's important to carefully evaluate the specific requirements of the system before choosing a load balancing solution. It's also important to consider the costs and benefits of load balancing, and to understand the specific trade-offs that may be involved.