Data Partition and Sharding
Data partitioning is the process of dividing a large dataset into smaller, more manageable pieces. The goal of data partitioning is to improve the performance and scalability of a system by reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored and retrieved by a single server or database.
There are various ways to partition data, but to keep this section relevant, we will only discuss two ways of partitioning data: horizontal partitioning and vertical partitioning.
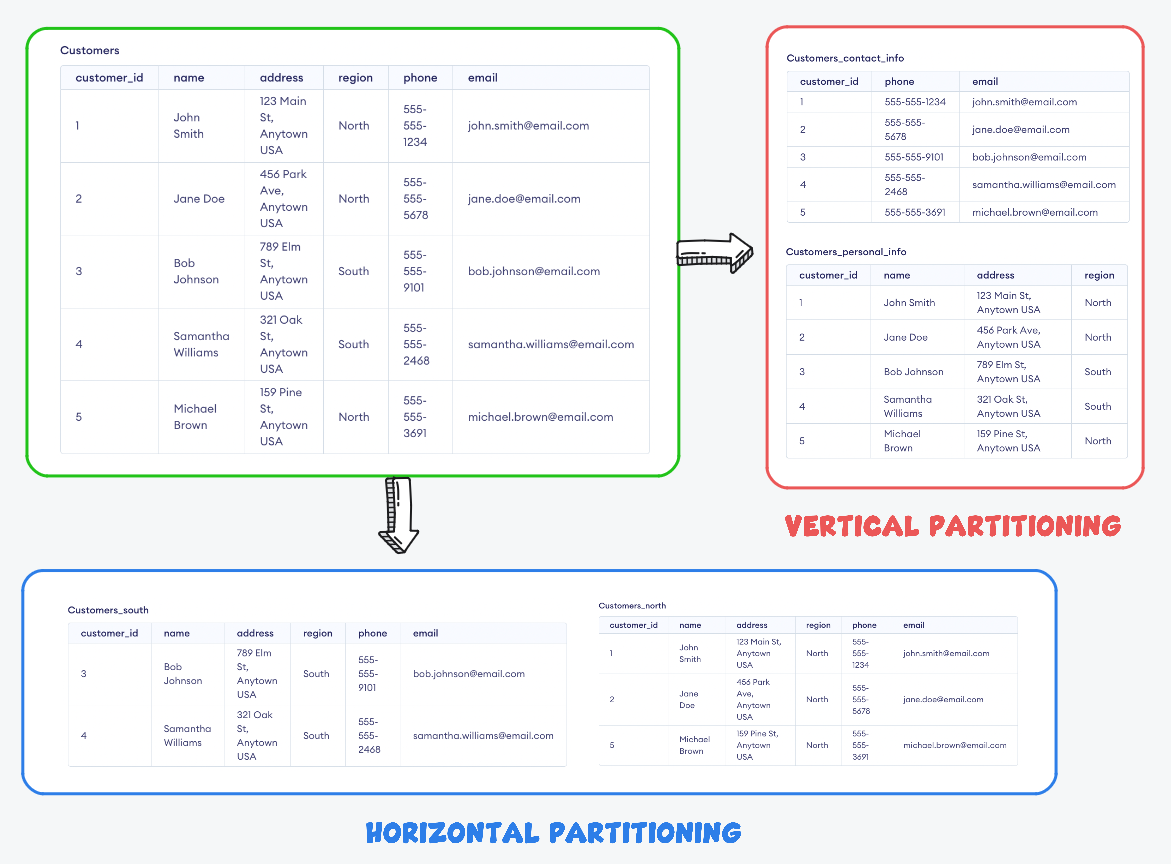
Vertical Partitioning:
Vertical partitioning, also known as column partitioning, refers to the process of dividing a table into multiple smaller tables, where each table contains a subset of the original table's columns. For example, if a table contains customer information, vertical partitioning could be used to create multiple smaller tables, each containing the information for a specific subset of columns such as personal information, address, and purchase history. This allows for faster retrieval of data as the partition containing the data can be quickly located based on the column value.
Horizontal Partitioning:
Horizontal partitioning, also known as row partitioning, refers to the process of dividing a table into multiple smaller tables, where each table contains a subset of the original table's rows. For example, if a table contains customer information, horizontal partitioning could be used to create multiple smaller tables, each containing the information for a specific subset of customers. This allows for faster retrieval of data as the partition containing the data can be quickly located based on the row value.
Sharding:
Sharding and partitioning are both techniques used to break up a large data set into smaller subsets, but they differ in how the data is distributed.
Sharding is the process of storing data records across multiple machines and is used when a single machine is not able to handle the amount of data and load of a high-traffic application. The data is partitioned horizontally across multiple machines, each machine stores a subset of the total data.
In a sharded system, data is partitioned into smaller chunks called shards. Each shard is then stored on a separate server or database. The process of partitioning the data is typically done based on a specific key or set of keys, such as a user ID or timestamp. This allows for faster retrieval of data as the shard containing the data can be quickly located based on the key value.
Partitioning, on the other hand, is a technique used to divide a large database into smaller, more manageable chunks within a single system.
It's worth noting that sharding is a more advanced technique than partitioning, and it requires careful planning and implementation to ensure that the data is distributed evenly across the shards and that the sharding key is chosen carefully to ensure that the data is distributed in a balanced way.